The Trie data structure
Mohanad Alrwaihy
March 29, 2023
78
3
A prefix of strings data structure
5 min read
What is a Trie?
In simple terms, Trie data structure is a String handling data structure that is based on the Prefix of string (Digital tree, Prefix tree) and it is used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings.
Applications 🚀
- Auto Complete
- Search Words
- Spell Checkers
- Browser History
Features ⚡
Trie is special because it's so fast. When searching for a word that starts with A you are going to eliminate all the words that don't start with A and if you are looking for the word App you are going to reduce the time it takes to find the word tremendously instead of using an Array to save the list of words.
Trie Example
A regular Trie consists of the following:
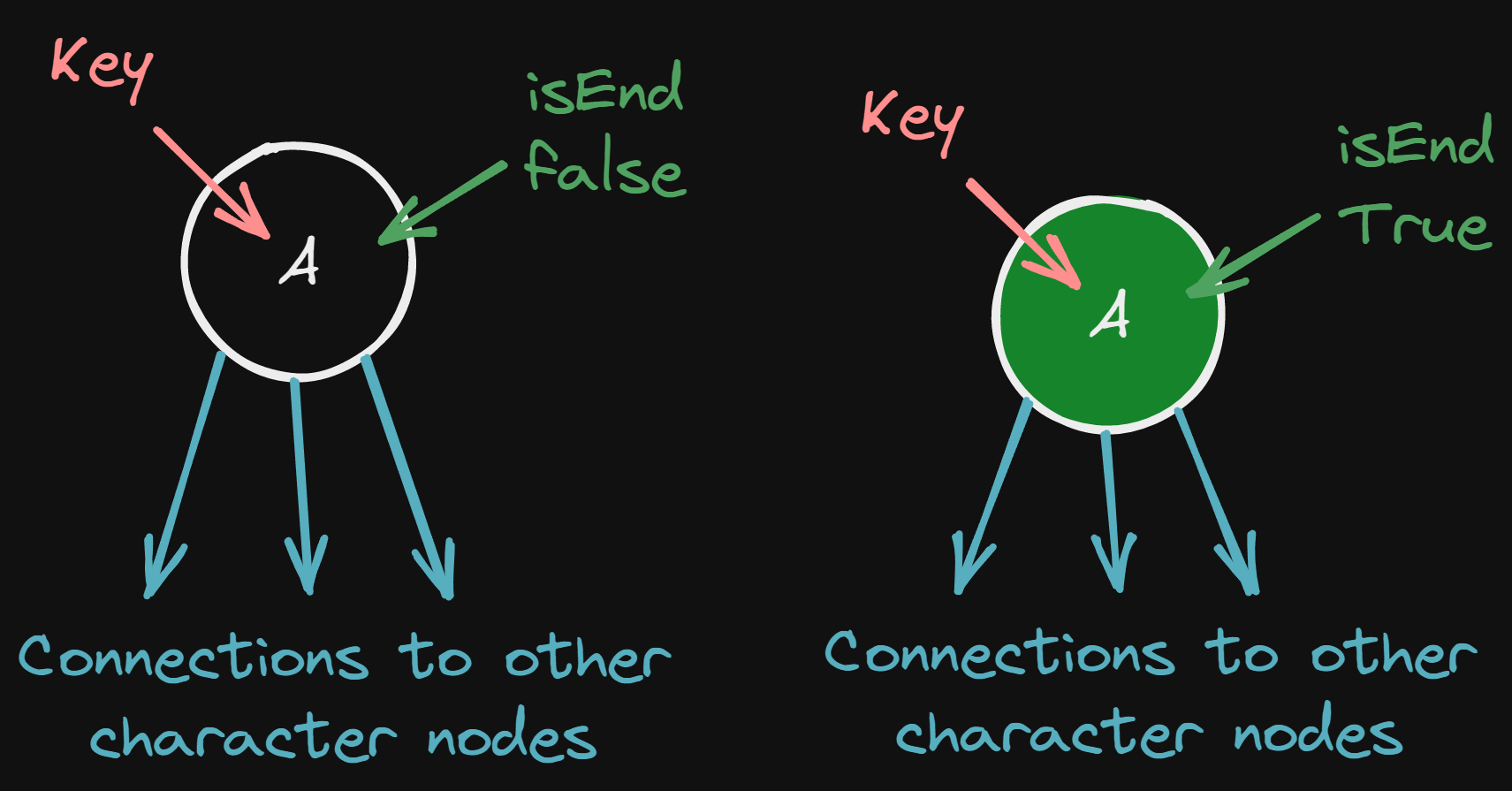
Root- This is the initial positionTrieNode- Each character is represented using a Node which has two properties:Child- Which has the current Node value and the connections to other nodes.IsEnd- A Boolean that can be set to true if the current Node is the last character of a word and a word can be formed here.
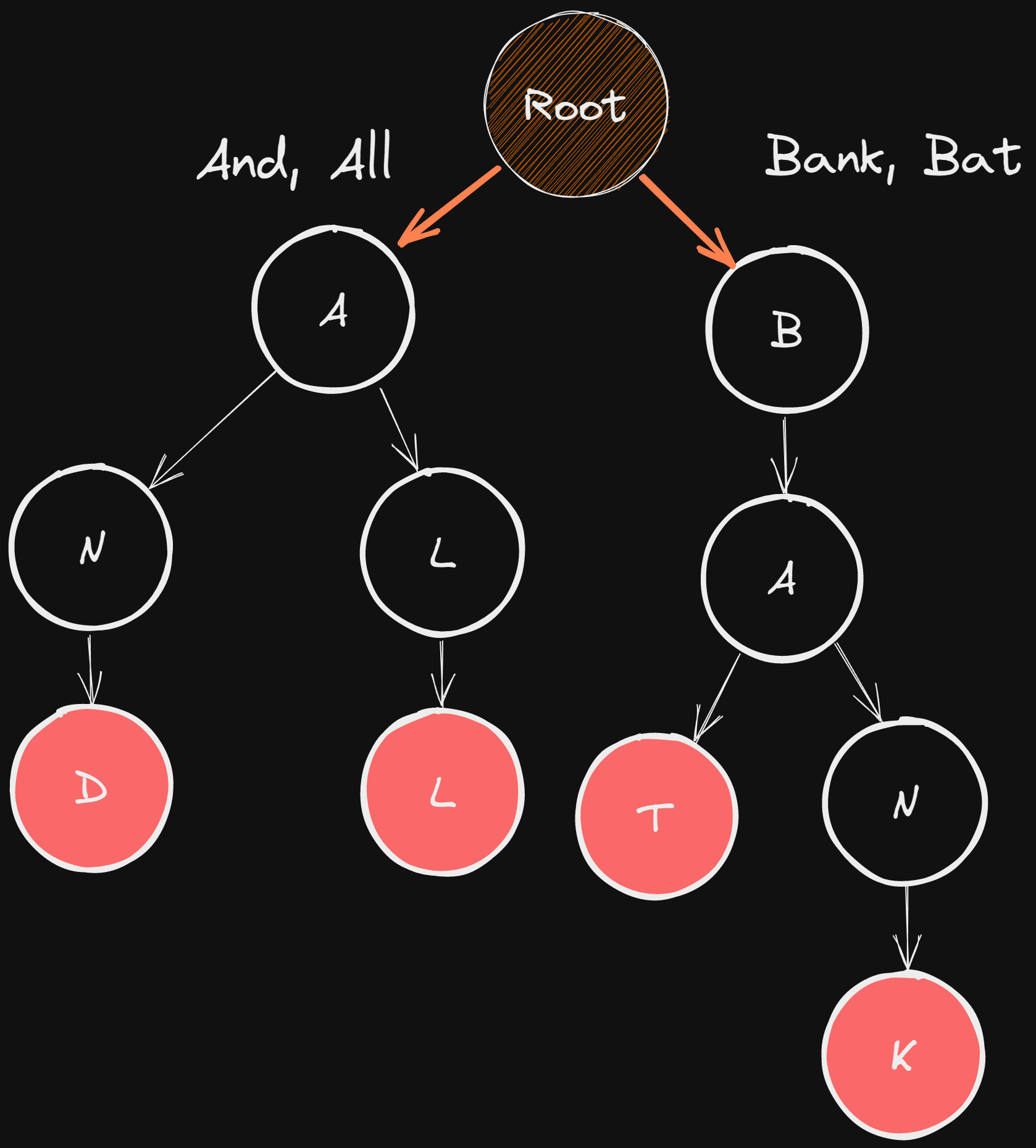
Here is an example of a Trie consisting of four words (And, All, Bank, Bat) and it shows the Trie structure and how we can traverse the Tree and know where the words are:
LeetCode Problems 🔨
To implement the Trie data structure I'm going to use two problems from LeetCode to show how we can implement Trie and use it to solve a real problem.
Problem 1: Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
Check the problem details Here.
Question Requirements:
Implement the Trie class:
Trie()Initializes the Trie object.void insert(String word)Inserts the stringwordinto theTrie.boolean search(String word)Returnstrueif the stringwordis in theTrie(i.e., was inserted before), andfalseotherwise.boolean startsWith(String prefix)Returnstrueif there is a previously inserted stringwordthat has the prefix, andfalseotherwise.
Solutions Steps 🪜
Step 1: Initialize the TrieNode:
To create a Trie first we are going to create a class named TrieNode which is the representation of a character node that holds the character Value, Children, isEnd:
TYPESCRIPTclass TrieNode {
constructor(child = {}, isEnd = false) {
this.child = child
this.isEnd = isEnd
}
}By default the TrieNode will start without any children and isEnd is going to be False until we insert words and trigger the last character of the word TrieNode to be True.
Visualization of TrieNode:
Step 2: Initialize the Trie (Prefix Tree):
The Trie class is going to be initiated with a list set to a new TrieNode that represents the Root.
TYPESCRIPTclass Trie {
constructor() {
this.list = new TrieNode()
}
}The start of a new Trie instance:
Step 3: Add Trie Functions:
We have three functions we want to add to the Trie class:
TYPESCRIPT// Insert new word to the list
insert(word: string): void {}
// Search for a word in the list
search(word: string): boolean {}
// Search if there is a word that start with specific set of characters.
startsWith(prefix: string): boolean {}
Let's now explain how to add words to the list and use the search functions to search the Trie.
Insert:
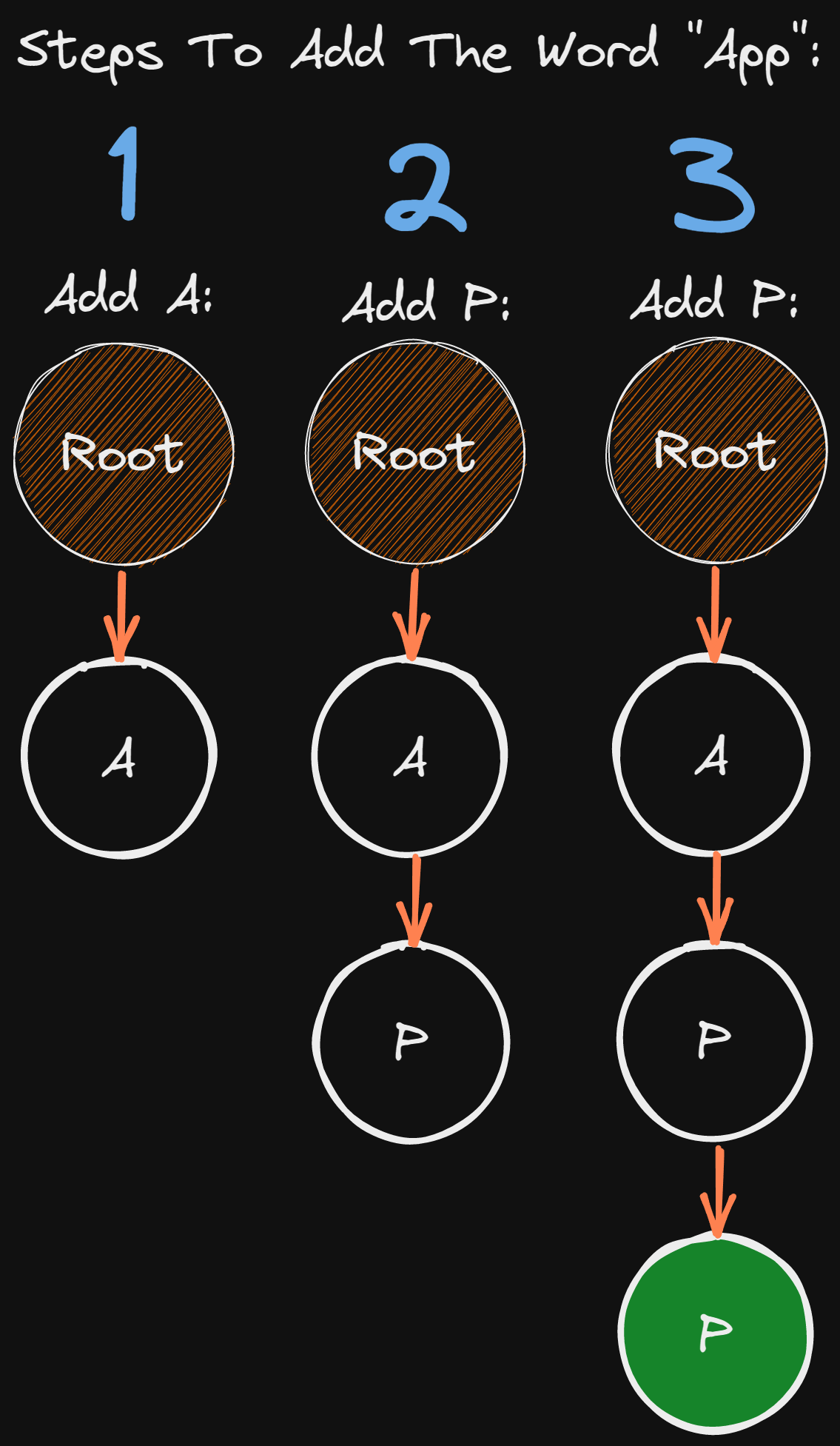
To insert the word App in our list we need to loop through the characters of the word and for each character we check if there is a TrieNode exists so we access and continue, or create a new TrieNode for the specific character.
Steps:
- Create a variable
nodeto access the nodes in the list. - Loop over the characters of the word App.
- Check if the character exists in the List.
- If the character does not exist create a new
TrieNode
- If the character does not exist create a new
- Access the next node character.
- Set the last character
isEndtoTrue.
TYPESCRIPTinsert(word: string): void {
let node = this.list
for (const char of word) {
if (!node[char]){
node[char] = new TrieNode()
}
node = node[char]
}
node.isEnd = true
}Search:
We can follow the same pattern of inserting the word but while searching we have to check for every character to see if there is a TrieNode or not and if there is not we can return False immediately.
Steps:
- Create a variable
nodeto access the nodes in the list. - Loop over the characters of the word.
- Check if the character exists in the List.
- If the character does not exist return
False
- If the character does not exist return
- Access the next node character.
- Return
Trueif theisEndof the last character isTrueelse returnFalse.
TYPESCRIPTsearch(word: string): boolean {
let node = this.list
for (const char of word) {
if (!node[char]) return false
node = node[char]
}
return node.isEnd
}StartsWith:
We can follow exactly the Search function steps but in the end, we are going to return True whether a word exists at the end of the prefix of not.
Steps:
- Create a variable
nodeto access the nodes in the list. - Loop over the characters of the word.
- Check if the character exists in the List.
- If the character does not exist return
False
- If the character does not exist return
- Access the next node character.
- Return
True.
TYPESCRIPT startsWith(prefix: string): boolean {
let node = this.list
for (const char of prefix){
if (!node[char]) return false
node = node[char]
}
return true
}